Práctica Computacional:
Introducción a Mathematica
Introducción
Mathematica se puede correr en 2 modos, uno es ``textual" y se corre
mediante el comando math, y el otro es ``gráfico" y se
corre con el comando mathematica.
La mejor forma de aprender rápidamente a usar el
Mathematica es practicando ejemplos.
En este caso hemos tomado los ejemplos mas simples del
Mathematica Tour ,
que recomendamos seguir en detalle.
Otra recomendación que damos, es utilizar el Help que existe en
el mismo programa, donde se pueden encontrar estos mismos ejemplos y
documentación detallada de cada sentencia.
Ejemplos
Mathematica como calculadora
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_1.gif]](Images/tour_gr_1.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_2.gif]](Images/tour_gr_2.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_3.gif]](Images/tour_gr_3.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_4.gif]](Images/tour_gr_4.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_5.gif]](Images/tour_gr_5.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_6.gif]](Images/tour_gr_6.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_7.gif]](Images/tour_gr_7.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_8.gif]](Images/tour_gr_8.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_9.gif]](Images/tour_gr_9.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_10.gif]](Images/tour_gr_10.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_11.gif]](Images/tour_gr_11.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_12.gif]](Images/tour_gr_12.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_13.gif]](Images/tour_gr_13.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_14.gif]](Images/tour_gr_14.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_15.gif]](Images/tour_gr_15.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_16.gif]](Images/tour_gr_16.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_17.gif]](Images/tour_gr_17.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_18.gif]](Images/tour_gr_18.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_19.gif]](Images/tour_gr_19.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_20.gif]](Images/tour_gr_20.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_21.gif]](Images/tour_gr_21.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_22.gif]](Images/tour_gr_22.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_23.gif]](Images/tour_gr_23.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_24.gif]](Images/tour_gr_24.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_25.gif]](Images/tour_gr_25.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_26.gif]](Images/tour_gr_26.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_27.gif]](Images/tour_gr_27.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_28.gif]](Images/tour_gr_28.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_29.gif]](Images/tour_gr_29.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_30.gif]](Images/tour_gr_30.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_31.gif]](Images/tour_gr_31.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_32.gif]](Images/tour_gr_32.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_33.gif]](Images/tour_gr_33.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_34.gif]](Images/tour_gr_34.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_35.gif]](Images/tour_gr_35.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_36.gif]](Images/tour_gr_36.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_37.gif]](Images/tour_gr_37.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_38.gif]](Images/tour_gr_38.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_39.gif]](Images/tour_gr_39.gif)
Algoritmos en Mathematica
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_40.gif]](Images/tour_gr_40.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_41.gif]](Images/tour_gr_41.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_42.gif]](Images/tour_gr_42.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_43.gif]](Images/tour_gr_43.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_44.gif]](Images/tour_gr_44.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_45.gif]](Images/tour_gr_45.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_46.gif]](Images/tour_gr_46.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_47.gif]](Images/tour_gr_47.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_48.gif]](Images/tour_gr_48.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_49.gif]](Images/tour_gr_49.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_50.gif]](Images/tour_gr_50.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_51.gif]](Images/tour_gr_51.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_52.gif]](Images/tour_gr_52.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_53.gif]](Images/tour_gr_53.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_54.gif]](Images/tour_gr_54.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_55.gif]](Images/tour_gr_55.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_56.gif]](Images/tour_gr_56.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_57.gif]](Images/tour_gr_57.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_58.gif]](Images/tour_gr_58.gif)
Converted by Mathematica
Problemas Sugeridos
- Calcular la función
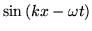 entre 0 y
entre 0 y 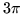 para
distintos valores de
para
distintos valores de 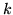 y
y 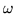 , en función de
, en función de 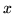 y de
y de 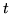
- Grabar los resultados en un archivo
- Leer los resultados del archivo
- Hacer una película, en la cual se vea la onda avanzando.
- Diagonalizar una matriz
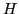 tridiagonal simétrica,
cuyos elementos son
tridiagonal simétrica,
cuyos elementos son
- Dibujar las primeras 3 autofunciones
(sus autovalores son los mas bajos)
- Aproximar la autofunción con autovalor mas bajo con una
función exponencial.
- Dibujar los Polinomios de Hermite, multiplicarlos por la exponencial
anterior, y comparar los resultados con las autofunciones obtenidas.
Darío Mitnik
U.B.A.
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_1.gif]](Images/tour_gr_1.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_1.gif]](Images/tour_gr_1.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_2.gif]](Images/tour_gr_2.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_4.gif]](Images/tour_gr_4.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_5.gif]](Images/tour_gr_5.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_7.gif]](Images/tour_gr_7.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_9.gif]](Images/tour_gr_9.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_11.gif]](Images/tour_gr_11.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_12.gif]](Images/tour_gr_12.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_14.gif]](Images/tour_gr_14.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_15.gif]](Images/tour_gr_15.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_17.gif]](Images/tour_gr_17.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_19.gif]](Images/tour_gr_19.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_20.gif]](Images/tour_gr_20.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_22.gif]](Images/tour_gr_22.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_24.gif]](Images/tour_gr_24.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_26.gif]](Images/tour_gr_26.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_27.gif]](Images/tour_gr_27.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_29.gif]](Images/tour_gr_29.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_30.gif]](Images/tour_gr_30.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_32.gif]](Images/tour_gr_32.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_33.gif]](Images/tour_gr_33.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_34.gif]](Images/tour_gr_34.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_35.gif]](Images/tour_gr_35.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_37.gif]](Images/tour_gr_37.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_38.gif]](Images/tour_gr_38.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_39.gif]](Images/tour_gr_39.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_40.gif]](Images/tour_gr_40.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_41.gif]](Images/tour_gr_41.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_43.gif]](Images/tour_gr_43.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_44.gif]](Images/tour_gr_44.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_46.gif]](Images/tour_gr_46.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_47.gif]](Images/tour_gr_47.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_49.gif]](Images/tour_gr_49.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_50.gif]](Images/tour_gr_50.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_52.gif]](Images/tour_gr_52.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_53.gif]](Images/tour_gr_53.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_55.gif]](Images/tour_gr_55.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_57.gif]](Images/tour_gr_57.gif)
![[Graphics:Images/tour_gr_58.gif]](Images/tour_gr_58.gif)