|
Big Bell Test - Buenos Aires
Final Results of CHSH correlation measurements for The Big Bell Test Experiment
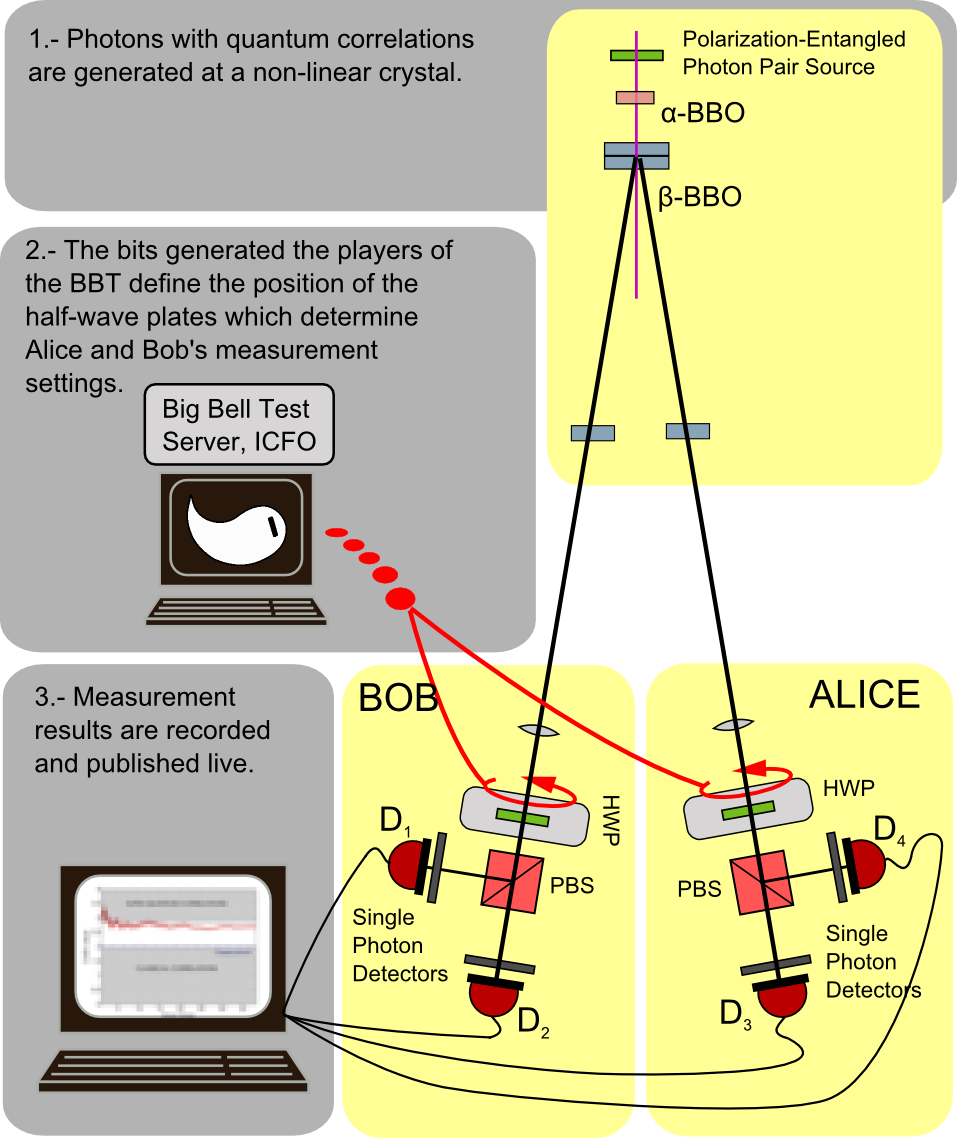
We performed a two-channel experiment to test a Clauser-Horne-Shimony-Holt (CHSH)-like inequality, using polarization entangled photons generated by spontaneous parametric downconversion in a BBO crystal arrangement. A series of birrefringence compensating crystals included in the photon pair source guarantee a high level of entanglement. Polarization projections are performed with motorized waveplates, which are fed with the random strings generated at the BBT cloud infrastructure. Two single-photon counting devices on each side detect the incoming photons, and send the detections to an FPGA based coincidence counter.
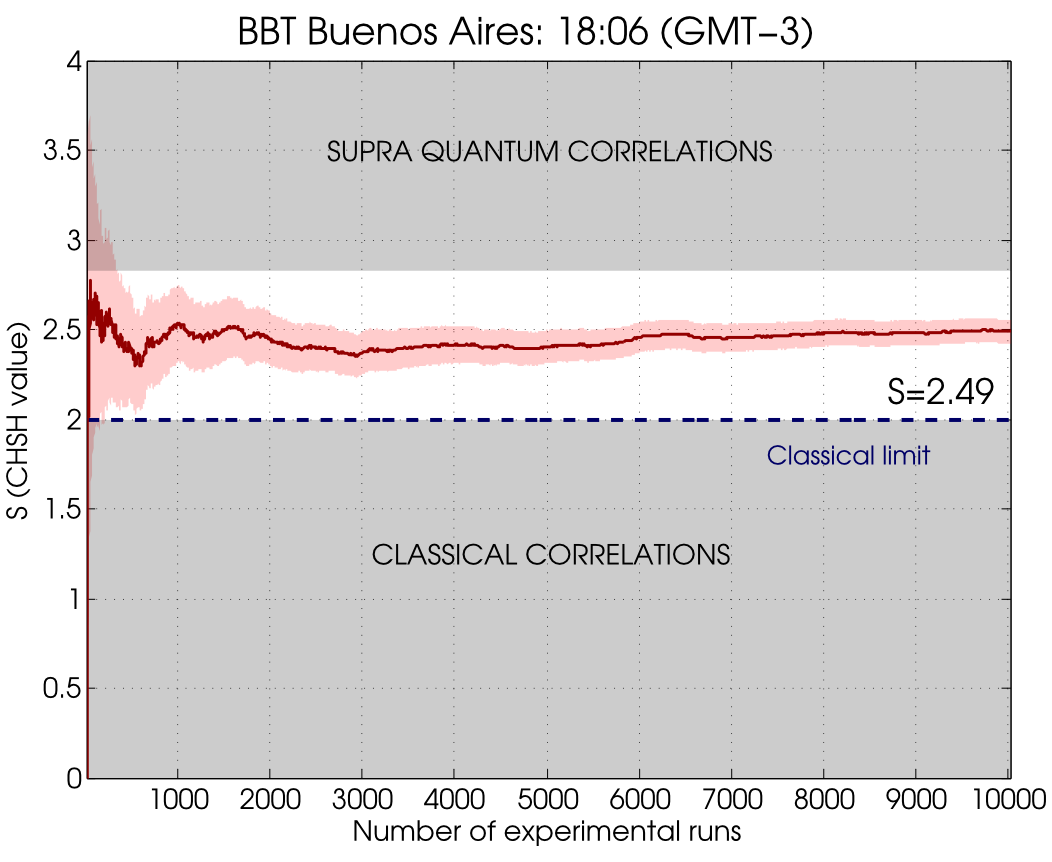
The experiment was automated and controlled from a single PC. Each experimental run consisted in the following sequence: a pair of random bits were gathered from the BBT server data and fed into the waveplate stepper motor drivers. Once the polarization projections were set, an FPGA-based coincidence counter started a repetition of 20 measurements on the four coincidence detections between D1&D3, D2&D3, D1&D4 and D2&D4. The brightness of our source and a detection window of 200μs for each measurement gave a single-channel coincidence probability below 0.1, thus minimizing the occurrence of multiple coincidences. The repetition of the measurement increased the chance of success of the measurement and therefore increased the "bit usage efficiency" of the experiment. We used the first single-channel coincidence from the list of 20 measurements as the result from each run. Overall, more than 20kbits were required from the BBT server at the Buenos Aires Node. The mean D1&D3 coincidence number per measurement was μ=0.091 for one particular waveplate setting. On the other hand, the mean success number of a single experiment (i.e. the expected value of detecting a coincidence on any channel during the 20 consecutive measurements) was ν=0.227. Statistics of occurrence of either of the above conditions follow a Poisson distribution. Runs with simultaneous coincidence detections on different channels were discarded. The final result from the long experiment run on November 30th, which built statistics from 10000 polarization settings, is an S-parameter value of S=2.488±0.016, which implies a violation of the CHSH-Bell inequality by more than 30 standard deviations!!. The experiment was performed at the Grupo de Optica Cuántica of DEILAP (CITEDEF-CONICET) in colaboration with the Quantum Foundations and Information Group of DF-FCEyN-UBA. Laura Knoll, Ignacio López Grande, Agustina Magnoni, Christian Schmiegelow, Ariel Bendersky and Miguel Larotonda (PI) are the BBT team at Buenos Aires.
|